
Before trying any of the above strategies, it’s important to understand whether they’ll fit your budget. Finally, the debt-to-equity ratio does not take into account when a debt is due. A debt due in the near term could have an outsized effect on the debt-to-equity ratio.
- You can calculate the debt ratio of a company from its financial statements.
- Many startups make high use of leverage to grow, and even plan to use the proceeds of an initial public offering, or IPO, to pay down their debt.
- In contrast, industries like technology or services, which require less capital, tend to have lower D/E ratios.
- On the other hand, businesses with D/E ratios too close to zero are also seen as not leveraging growth potential.
- Not only that, companies with a high debt-to-equity ratio may have a hard time working with other lenders, partners, or even suppliers, who may be afraid they won’t be paid back.
Best for low interest rate: Third Federal Savings and Loan
The depository industry (banks and lenders) may have high debt-to-equity ratios. Because banks borrow funds to loan money to consumers, financial institutions usually have higher debt-to-equity ratios than other industries. Current liabilities are the debts that a company will typically pay off within the year, including accounts payable. Long-term liabilities are debts whose maturity extends longer than a year. Not all debt is considered equally risky, however, and investors may want to consider a company’s long-term versus short-term liabilities.
Third Federal Savings and Loan
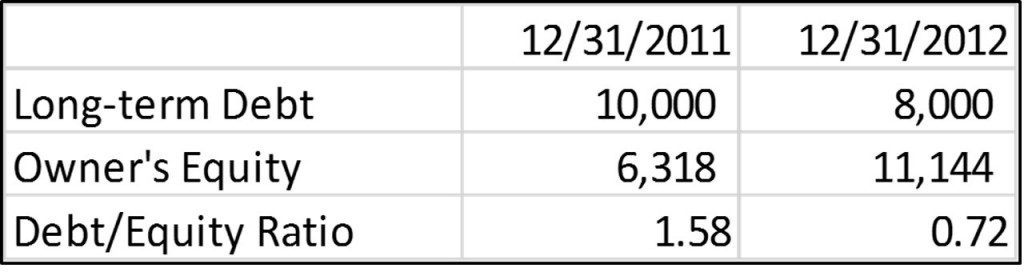
But if a company has grown increasingly reliant on debt or inordinately so for its industry, potential investors will want to investigate further. A D/E ratio of 1.5 would indicate that the company in question has $1.50 of debt for every $1 of equity. To illustrate, suppose the company had assets of $2 million and liabilities of $1.2 million. Because equity is equal to assets minus liabilities, the company’s equity would be $800,000. Its D/E ratio would therefore be $1.2 million divided by $800,000, or 1.5.
Debt-To-Equity Ratio Formula:
Analysts and investors compare the current assets of a company to its current liabilities. Over time, the cost of debt financing is usually lower than the cost of equity financing. This is because when a company takes out a loan, it only has to pay back the principal plus interest. For example, let us say a company needs $1,000 to finance its operations. If the company were to use equity financing, it would need to sell 100 shares of stock at $10 each.
Our top picks of timely offers from our partners
Some industries like finance, utilities, and telecommunications normally have higher leverage due to the high capital investment required. A D/E ratio close to zero can also be a negative sign as it indicates that the business isn’t taking advantage of the potential growth it can gain from borrowing. The debt-to-equity apps ratio is a way to assess risk when evaluating a company. The ratio looks at debt in relation to equity, providing insights into how much debt a company is using to finance its operations. In our debt-to-equity ratio (D/E) modeling exercise, we’ll forecast a hypothetical company’s balance sheet for five years.
Debt to equity ratio: Calculating company risk
Find out what a debt-to-equity ratio is, why it is important to a business, and how to calculate it. So in the case of deciding whether to invest in IPO stock, it’s important for investors to consider debt when deciding whether they want to buy IPO stock. This ratio compares a company’s equity to its assets, showing how much of the company’s assets are funded by equity. In order to calculate the debt-to-equity ratio, you need to understand both components.
The offers that appear on this site are from companies that compensate us. But this compensation does not influence the information we publish, or the reviews that you see on this site. We do not include the universe of companies or financial offers that may be available to you. A debt-to-equity ratio of between 1 and 1.5 is good for most businesses, but some industries are capital intensive and businesses in these industries traditionally take on more debt. A debt-to-equity ratio that is too high suggests the company may be relying too much on lending to fund operations. This makes investing in the company riskier, as the company is primarily funded by debt which must be repaid.
Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others. Our team of reviewers are established professionals with decades of experience in areas of personal finance and hold many advanced degrees and certifications. At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content.
Business owners use a variety of software to track D/E ratios and other financial metrics. Microsoft Excel provides a balance sheet template that automatically calculates financial ratios such as the D/E ratio and the debt ratio. To get a clearer picture and facilitate comparisons, analysts and investors will often modify the D/E ratio. They also assess the D/E ratio in the context of short-term leverage ratios, profitability, and growth expectations. If a company cannot pay the interest and principal on its debts, whether as loans to a bank or in the form of bonds, it can lead to a credit event.
Join the conversation